Night vision technology has evolved significantly over the years, and with the advent of digital technology, it has become more advanced, efficient, and affordable. Digital night vision is a cutting-edge technology that enables users to capture high-quality images and videos in low-light conditions, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, from hunting and surveillance to security and wildlife observation.
In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive guide to digital night vision technology, covering its history, technology, applications, advantages, and limitations. So, let's dive in and explore the fascinating world of digital night vision!
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. A Brief History of Night Vision Technology
- 3. Digital Night Vision Technology Explained
- 4. How Digital Night Vision Works
- 5. Types of Digital Night Vision Devices
- 5.1 Digital Night Vision Binoculars
- 5.2 Digital Night Vision Scopes
- 5.3 Digital Night Vision Monoculars
- 6. Advantages of Digital Night Vision
- 6.1 High-Quality Imaging
- 6.2 Low-Light Sensitivity
- 6.3 Cost-Effective
- 6.4 Lightweight and Portable
- 6.5 Easy to Use
- 7. Limitations of Digital Night Vision
- 7.1 Limited Range and Field of View
- 7.2 Dependence on Ambient Light
- 7.3 Battery Life
- 7.4 Vulnerability to Glare and Overexposure
- 8. Applications of Digital Night Vision
- 8.1 Hunting and Wildlife Observation
- 8.2 Security and Surveillance
- 8.3 Law Enforcement and Military
- 8.4 Astronomy and Astrophotography
- 9. Choosing the Right Digital Night Vision Device
- 9.1 Budget and Purpose
- 9.2 Magnification and Objective Lens
- 9.3 Image Quality and Resolution
- 9.4 Field of View and Range
- 9.5 Additional Features and Accessories
- 10. Tips for Using Digital Night Vision
- 10.1 Adjusting the Brightness and Contrast
- 10.2 Using IR Illuminators
- 10.3 Avoiding Overexposure and Glare
- 10.4 Maintaining the Device
- 11. Conclusion
- 12. FAQs
Introduction
Digital night vision technology is a game-changer when it comes to low-light imaging, enabling users to capture high-quality images and videos even in complete darkness. Unlike traditional night vision devices that rely on intensifier tubes to amplify ambient light, digital night vision uses sensors and digital processing to capture and enhance images, providing clear and detailed visuals in a wide range of environments.
Digital night vision is becoming increasingly popular among outdoor enthusiasts, hunters, law enforcement agencies, and military personnel, thanks to its affordability, efficiency, and portability. Moreover, the technology has been constantly evolving, with new devices and features being introduced regularly, making it more accessible and versatile.
In this article, we'll take a closer look at digital night vision technology, exploring its history, technology, applications, advantages, and limitations. We'll also provide tips on how to choose and use a digital night vision device, helping you get the most out of this cutting-edge technology.
A Brief History of Night Vision Technology
Night vision technology dates back to the early 20th century, when the first infrared-sensitive devices were developed. These early devices used infrared radiation to detect objects in the dark. The technology has since evolved to include various forms of night vision, including thermal imaging and digital night vision.

During World War II, night vision technology became critical for military operations, leading to the development of image intensification technology. This technology amplified available light, making it possible for soldiers to see in low-light conditions.
In the 1960s, thermal imaging technology was introduced, which detects and captures the heat radiating from objects. This technology allowed users to see through darkness, smoke, and fog, making it ideal for military and law enforcement applications.
Digital night vision technology emerged in the 1990s, offering a more affordable and versatile alternative to traditional night vision devices. By the 2000s, digital night vision devices had become widespread, with new features and capabilities being added to enhance their performance and usability.
Today, digital night vision technology is widely used in various fields, from hunting and wildlife observation to law enforcement and surveillance. Its versatility, portability, and affordability make it a popular choice for anyone who needs to see in low-light conditions.
Digital Night Vision Technology Explained
Digital night vision technology is based on digital image sensors and processing, which capture and enhance available light, converting it into high-quality images and videos. Unlike traditional night vision devices that use intensifier tubes to amplify ambient light, digital night vision devices use sensors and processors to create images in real-time.
Digital night vision devices come in a variety of forms, including binoculars, monoculars, and scopes, each with its own set of features and capabilities. These devices are used in a wide range of applications, from hunting and wildlife observation to surveillance and law enforcement.
How Digital Night Vision Works
Digital night vision devices work by capturing and processing available light, converting it into high-quality images and videos. They use a combination of sensors, lenses, and processors to create images in real-time, providing users with a clear and detailed view of their surroundings.
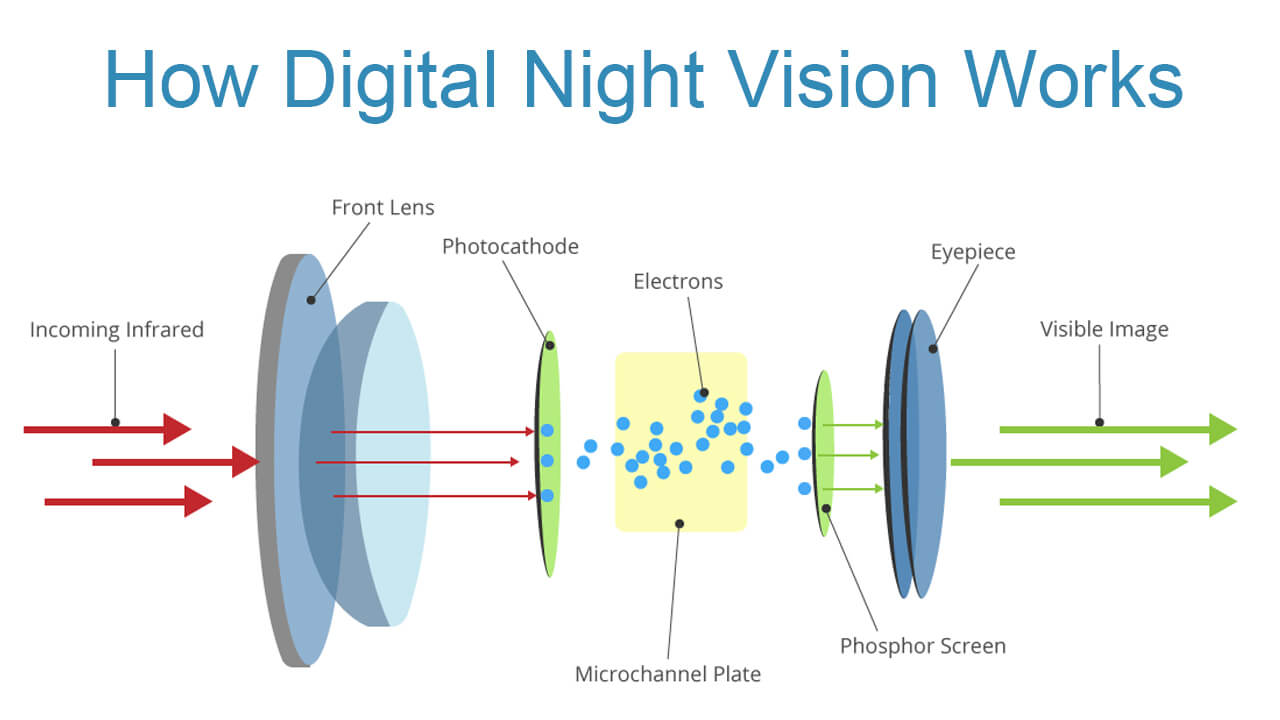
Digital night vision devices use either CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) or CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) sensors to capture light. These sensors convert light into electrical signals, which are then processed by the device's onboard processor.
The processor enhances the images by adjusting contrast, brightness, and color, resulting in a clear and detailed view of the environment. Some digital night vision devices also use infrared (IR) illuminators to enhance low-light imaging, emitting IR light that is invisible to the human eye but visible to the device's sensors.
Types of Digital Night Vision Devices
Digital night vision devices come in several forms, each with its own set of features and capabilities. The most common types of digital night vision devices include binoculars, scopes, and monoculars.
5.1 Digital Night Vision Binoculars
Digital night vision binoculars are ideal for observing wildlife, hunting, and surveillance applications. They typically have two eyepieces and a central focusing knob, allowing users to adjust the focus and magnification.

Digital night vision binoculars usually have a wider field of view than monoculars, making them ideal for scanning large areas quickly. They also often have longer battery life and larger objective lenses, providing better low-light imaging.
5.2 Digital Night Vision Scopes
Digital night vision scopes are typically used for hunting and tactical applications, mounted on rifles or other firearms. They allow users to aim and shoot accurately in low-light conditions, with crosshairs or reticles superimposed on the image.

Digital night vision scopes usually have a higher magnification than binoculars or monoculars, allowing users to see objects at a greater distance. They also often have more durable construction, with shock-resistant and waterproof features.
5.3 Digital Night Vision Monocular
Digital night vision monocular are the most compact and portable form of digital night vision devices. They are ideal for handheld applications, such as hiking, camping, or surveillance.

Digital night vision monoculars usually have a single eyepiece and a smaller objective lens than binoculars or scopes, making them more portable and lightweight. They often have a built-in IR illuminator, providing better low-light imaging.
Advantages of Digital Night Vision Technology
Digital night vision technology offers several advantages over traditional night vision devices, including:
6.1 High-Quality Imaging
One of the most significant advantages of digital night vision is the high-quality imaging it offers. Digital sensors capture more light and provide clearer, sharper images than analog technology. This allows users to see fine details and colors in low-light conditions.
6.2 Low-Light Sensitivity
Digital night vision devices are highly sensitive to low-light conditions, making them ideal for use in complete darkness. They can amplify the available light and make even the darkest scenes visible.
6.3 Cost-Effective
Digital night vision technology is becoming increasingly cost-effective, making it more accessible to consumers. While high-end digital night vision devices can still be expensive, many entry-level models are now available at an affordable price.
6.4 Lightweight and Portable
Digital night vision devices are typically lighter and more portable than traditional night vision devices. They can be easily carried in a pocket or backpack, making them ideal for outdoor activities like hunting and camping.
6.5 Easy to Use
Digital night vision devices are generally very user-friendly. Many models feature simple controls and intuitive menus, making them easy to operate even for those with little experience.
Limitations of Digital Night Vision
While digital night vision devices offer several advantages, they also have some limitations that should be taken into account.
7.1 Limited Range and Field of View
Digital night vision devices typically have a limited range and field of view compared to traditional night vision devices. This can make it difficult to see distant objects or large areas.
7.2 Dependence on Ambient Light
Digital night vision devices rely on ambient light to produce an image. If there is no ambient light, such as in a completely dark environment, the device will not be able to function.
7.3 Battery Life
Digital night vision devices require a power source to operate, and the battery life can be limited. Users should be aware of the expected battery life of their device and carry spare batteries if needed.
7.4 Vulnerability to Glare and Overexposure
Digital night vision devices can be vulnerable to glare and overexposure, which can produce bright spots in the image and reduce visibility. Care should be taken to avoid pointing the device directly at bright light sources.
Applications of Digital Night Vision
Digital night vision technology has a wide range of applications across various industries and activities.
8.1 Hunting and Wildlife Observation

Digital night vision devices are popular among hunters and wildlife enthusiasts, as they allow users to observe nocturnal animals without disturbing them. They are also useful for navigating in low-light conditions.
8.2 Security and Surveillance

Digital night vision devices are commonly used in security and surveillance applications. They can provide high-quality imaging in low-light conditions, making it easier to monitor areas and detect intruders.
8.3 Law Enforcement and Military

Digital night vision technology is widely used by law enforcement and military personnel for surveillance and tactical operations. It allows them to see in low-light conditions and maintain a tactical advantage.
8.4 Astronomy and Astrophotography

Digital night vision devices can be used for astronomy and astrophotography, allowing users to capture clear images of celestial objects in low-light conditions.
Choosing the Right Digital Night Vision Device
When selecting a digital night vision device, there are several factors to consider.
9.1 Budget and Purpose
The first factor to consider is the budget and intended purpose of the device. Entry-level models are available at a lower price point but may not have all the features and capabilities of high-end devices.
9.2 Magnification and Objective Lens
The magnification of the device determines the size of the image seen through the lens. Higher magnification levels provide a closer look at the target, but they may reduce the field of view and make it harder to spot moving objects. The objective lens, on the other hand, determines the amount of light that enters the device, which affects the brightness and clarity of the image. Larger objective lenses collect more light and produce brighter images, but they may also make the device heavier and more expensive.
9.3 Image Quality and Resolution
The image quality and resolution are crucial factors to consider when choosing a digital night vision device. High-quality sensors and optics can produce sharp and clear images even in low-light conditions. The resolution is the number of pixels that make up the image, and higher resolutions provide more details and better image quality. However, higher resolutions also require more processing power and may reduce the device's battery life.
9.4 Field of View and Range
The field of view refers to the area visible through the device's lens, and a wider field of view can make it easier to spot moving targets. The range of the device, on the other hand, is the maximum distance at which it can detect and identify objects. Longer ranges may require higher magnification levels and larger objective lenses, but they also provide more versatility and flexibility.
9.5 Additional Features and Accessories
Digital night vision devices may come with additional features and accessories that can enhance their functionality and convenience. Some common features include video recording capabilities, adjustable brightness and contrast, and the ability to switch between monochrome and color modes. Accessories like tripods, mounts, and carrying cases can also make it easier to use and transport the device.
Tips for Using Digital Night Vision
To get the most out of your digital night vision device, there are some tips and best practices to keep in mind. Here are some key tips to consider:
10.1 Adjusting the Brightness and Contrast
Different lighting conditions may require adjustments to the device's brightness and contrast settings. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance between brightness and image quality.
10.2 Using IR Illuminators
IR illuminators can provide additional light in low-light conditions, improving the device's performance. However, be aware that using IR illuminators may reduce the device's battery life and may also attract unwanted attention.
10.3 Avoiding Overexposure and Glare
Digital night vision devices can be vulnerable to glare and overexposure, especially in bright or reflective environments. To avoid these issues, try to position the device away from bright light sources and use the device's adjustable settings to reduce the glare.
10.4 Maintaining the Device
Proper maintenance can help ensure that your digital night vision device continues to perform at its best. Keep the lenses clean and free of debris, store the device in a dry and secure location, and replace the batteries as needed.
Conclusion
Digital night vision technology has revolutionized the way we see and perceive our surroundings in low-light conditions. With its affordability, versatility, and real-time imaging capabilities, digital night vision devices have become widely used in a variety of applications, from hunting and wildlife observation to surveillance and law enforcement.
Whether you are a hunter, a nature enthusiast, or a law enforcement officer, digital night vision devices can enhance your experience and help you see the world in a new light.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can digital night vision devices be used during the day?
Most digital night vision devices are not recommended for use during the day, as the bright sunlight can damage the sensors and processors. However, some devices have a day/night mode, allowing them to be used in both daylight and low-light conditions.
2. How far can digital night vision devices see?
The range of digital night vision devices varies depending on the device and the ambient light conditions. Some devices can see up to several hundred yards in complete darkness, while others may have a shorter range.
3. Are digital night vision devices legal for hunting?
The legality of using digital night vision devices for hunting varies by state and country. It is important to check your local hunting regulations before using digital night vision devices for hunting.
4. How long do digital night vision device batteries last?
The battery life of digital night vision devices varies depending on the device and the battery type. Some devices can last several hours on a single charge, while others may require frequent battery changes.
5. How do I choose the right digital night vision device for my needs?
When choosing a digital night vision device, consider your intended use, such as hunting, surveillance, or wildlife observation. Also, consider factors such as image quality, magnification, and battery life, as well as your budget and personal preferences.








